My wavefunction
An abstract of my
theory:
My favorite equation:
I am the first in the world who wrote a link between science and spirituality.
The most important question: Who am I?
I found the answer:
”I am a wave and the wavefunction is:
|ψ> = c1 |Φ1> + c2|Φ2> + c3|Φ3> + c4|Φ4> + c5|Φ5> + c6|Φ6> + c7|Φ7>
are 7 states |Φi > because are 7 major chakras or energy centers.” Adrian Ferent
I am the first in the world who wrote a link between science and spirituality.
The most important question: Who am I?
I found the answer:
”I am a wave and the wavefunction is:
|ψ> = c1 |Φ1> + c2|Φ2> + c3|Φ3> + c4|Φ4> + c5|Φ5> + c6|Φ6> + c7|Φ7>
are 7 states |Φi > because are 7 major chakras or energy centers.” Adrian Ferent
A wavefunction is probability amplitude
in quantum mechanics describing the quantum state of a particle and how
it behaves. Its values are complex numbers and for a single particle, it is a
function of space and time.
An arbitrary state of potential will be written as
|ψ>
= a|1> + b|2>, |a|^2 + |b|^2 = 1
such that, after the process of projection, the probability
for either distinct state, namely
|1>
or |2> to become real is unity.
"I am a WAVE and the wave function is:
If the states |Φi > have distinct, definite values, a_i,
of some dynamical variable and a measurement of that variable is performed on a
system in the state
|ψ> = Σ ci | Φi
>
then the probability of measuring a_i is | ci |^2, and if
the measurement yields a_i, the system is left in the state |Φi > .
The wavefunction
is absolutely central to quantum mechanics. It is also the source of the
mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in what quantum
mechanics means in nature, and even how nature itself behaves at the atomic
scale and beyond.
It is
concerned mainly with giving the general outlines of a new way of thinking,
consistent with modern physics, which does not divide mind from matter, the
observer from the observed, the subject from the object. What is described here
is, only the beginning of such a way of thinking which, it is hoped, can be
developed a great deal further.
Descartes solved the problem by assuming that God, who
created both mind and matter is able to relate them by putting into the minds
of human beings the clear and distinct thoughts that are needed to deal with
matter as extended substance.
On the basis of modern physics even inanimate matter cannot
be fully understood in terms of Descartes' notion that it is nothing but a substance
occupying space and constituted of separate objects.
Between observations the wavefunction evolves
deterministically according to an evolution operator (constructed appropriately
for the particular problem) acting on an assumed initial state and the
wavefunction as a function of time has a typical oscillatory form, such as the
evolution of simple harmonic oscillator states.
The
quantum theory implies that all material systems have what is called a
wave-particle duality in their properties. In consequence, electrons that in
Newtonian physics act like particles can, under suitable conditions, also act
like waves.
Are 7 states |Φi > because are 7 major chakras or
energy centers:
|ψ> = Σ ci | Φi >
|ψ> is the wave function of each man, the unique chord
whether he be sleeping or waking, living or dead and he can always be found by
it.
In the early 1980's, various authors started to investigate
the generalization of information
theory concepts to allow the representation of information
by quantum states.
The introduction into computation of quantum physical
concepts, in particular the superposition principle, opened up the possibility
of new capabilities, such as quantum cryptography that have no classical
counterparts.
Environment can destroy coherence between the states of a
quantum system. This is decoherence. According to quantum theory, every
superposition of quantum states is a legal quantum state. This egalitarian
quantum principle of superposition applies in isolated systems.
However, not all quantum superpositions are treated equally
by decoherence. Interaction with the environment will typically single out a
preferred set of states.
About probabilities
Probability plays a role in almost all the sciences. In
epistemology, the philosophy of mind, and cognitive science, we see states of
opinion being modeled by subjective probability functions, and learning being
modeled by the updating of such functions.
An interpretation of the concept of probability is a choice
of some class of events and an assignment of some meaning to probability claims
about those events.
Subjective probability lacks the resources to distinguish
uncertainty due to lack of information from uncertainty that no possible
increase in knowledge could eliminate.
It can even take center stage in the philosophy of logic,
the philosophy of language, and the philosophy of religion. Probability is
thought of as a physical disposition, or tendency of a given type of physical
situation to yield an outcome of a certain kind, or to yield a long run
relative frequency of such an outcome.
Probability starts with logic. There is a set of N elements.
We can define a sub-set of n favorable elements, where n is less than or equal to
N. Probability is defined as the rapport of the favorable cases over total
cases.
That formulation makes it easier to understand why
probability can never be higher than 1: no event can have more than one success
in one try!
Problems in the foundations of probability bear at least
indirectly, and sometimes directly, upon central scientific, social scientific
and philosophical concerns.
Science furnishes
important examples of deterministic theories with such initial-condition
probabilities.
The interpretation of probability is one of the most
important such foundational problems.
In probability theory,
an event is a set of outcomes to which a probability is assigned.
An elementary event (or simple event) is an event which
contains only a single outcome in the same space.
For every event defined on S, we can define a
counterpart-event called its complement. The complement of an event A consists
of all outcomes that are in S, but are not in A: The key word in the definition
of a complement is not.
Let Ω be a non-empty set.
A field on Ω is a set F of subsets of Ω that has Ω as a
member, and that is closed under complementation (with respect to Ω) and union.
Let P be a function from F to the real numbers obeying:
(Non-negativity) P(A) ≥ 0, for all A ∈
F.
(Normalization) P(Ω) = 1.
(Finite additivity) P(A ∪
B) = P(A) + P(B) for all A, B ∈ F such that
A ∩ B = ∅.
Call P a probability function, and (Ω, F, P) a probability
space.
An interpretation of the concept of probability is a choice
of some class of events (or statements) and an assignment of some meaning to probability
claims about those events (or statements).
Probability theory is used extensively in statistics,
mathematics, science and philosophy to draw conclusions about the likelihood of
potential events and the underlying mechanics of complex systems.
The probability of a random event denotes the relative
frequency of occurrence of an experiment's outcome, when repeating the
experiment.
The probability of event A is the number of ways event A can
occur divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
Sure event occurs every time an experiment is repeated and
has the probability 1.
An event that never occurs when an experiment is performed
is called impossible event. The probability of an impossible event is 0.
Some standard properties of probability are the following:
If P(A ∩ B) = 0, then P(A ∪
B) = P(A) + P(B)
The complement of an event A is
the event [not A] (that is, the event of A not occurring):
P(CA) = 1 − P(A).
If A and B are in the domain of P, then A and B are
probabilistically independent (with respect to P) just in case P(A ∩ B) =
P(A)P(B).
A random variable for probability P is a function X that
takes values in the real numbers, such that for any number x, X = x is an event
in the domain of P. The conditional probability of A given B, written
P(A | B) is standard defined as follows:
P(A | B) = P(A ∩ B)/P(B).
If P(B) = 0, then the ratio in the definition of conditional
probability is undefined. There are, however, a variety of technical
developments that will allow us to define P(A | B) when P(B) is 0.
If the events are not mutually exclusive then:
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B)
The chakras and
probabilities
If the states |Φi > have distinct, definite values, a_i,
of some dynamical variable and a measurement of that variable is performed on a
system in the state
|ψ> = Σ ci | Φi
>
then the probability of measuring a_i is | ci |^2, and if
the measurement yields a_i, the system is left in the state |Φi > .
We have more than these 7 most important chakras, I will
consider the number of all chakras equal to n.
The wavefunction for the all n chakras:
”I am a
wave and the wavefunction is:
|ψ> = c1 |Φ1> + c2|Φ2> + c3|Φ3> + … + cn|Φn>
are n states |Φi > because are n chakras or energy centers.” Adrian Ferent
|ψ> = c1 |Φ1> + c2|Φ2> + c3|Φ3> + … + cn|Φn>
are n states |Φi > because are n chakras or energy centers.” Adrian Ferent
I will associate to each chakra an event:
E1 – the event associated to chakra 1(Muladhara); the
probability assigned is e1
E2 – the event associated to chakra 2; the probability
assigned is e2
………….
E3 – the event associated to chakra 3; the probability
assigned is e3
E7 – the event associated to chakra 7; the probability
assigned is e7 .
We have to see these 7 chakras as a system S.
When is activated only chakra 1, the event is X1
:
X1 = E1 ∩ CE2 ∩ CE3 ∩ CE4 ∩ CE5 ∩ CE6 ∩ CE7
I calculated the probability x1 for the event X1
:
Here is the probability to realize only one event, but any
event for the chakra system , S:
The event S = X1∪X2∪X3 ∪… ∪Xn
I calculated the probability assigned for this event, PS
:
The probability if any 2 chakras are activated in the same
time, for a system with n chakras, PS :
This means it is a lot of math, when you concentrate on
chakras!
Looks like Yoga is very complicated!
This means now we can have a precisely, exactly picture of
each individual aura, because we know the activity of each chakra.
In the future the health of each person will be checked by
analyzing the aura.
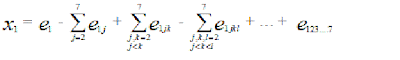




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.